BACKGROUND: Mesenchymal stem cells in the adult corneal stroma (named corneal stromal stem cells, CSSCs) inhibit corneal inflammation and scarring and restore corneal clarity in pre-clinical corneal injury models. This cell therapy could alleviate the heavy reliance on donor materials for corneal transplantation to treat corneal opacities. Herein, we established Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) protocols for CSSC isolation, propagation, and cryostorage, and developed in vitro quality control (QC) metric for in vivo anti-scarring potency of CSSCs in treating corneal opacities.
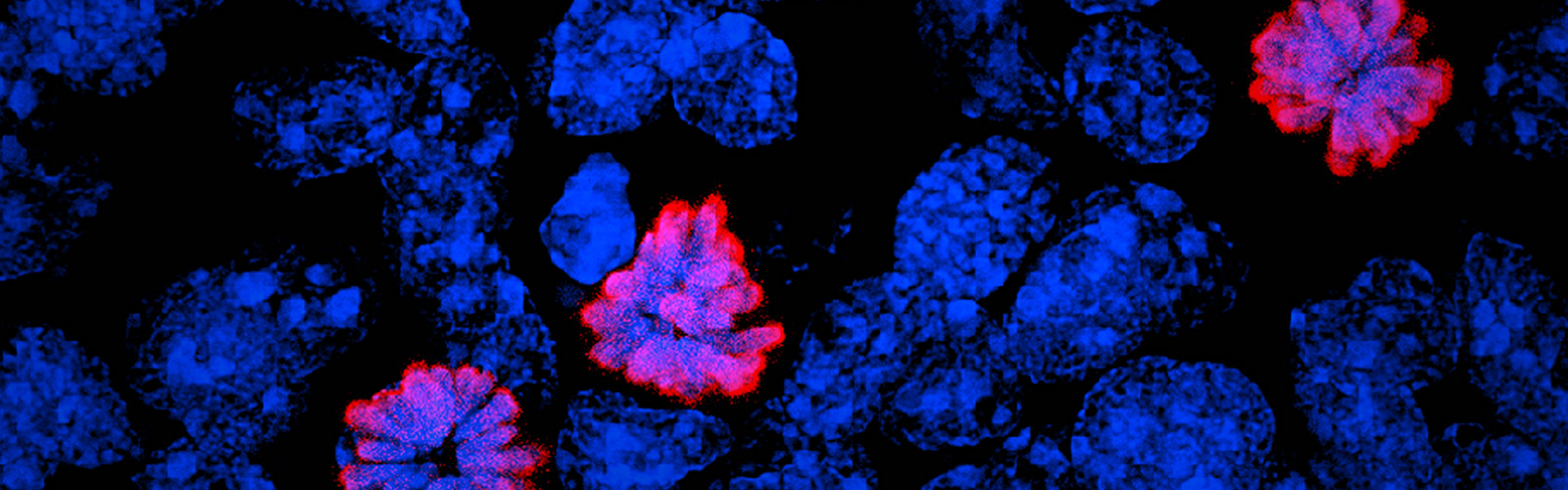
METHODS: A total of 24 donor corneal rims with informed consent were used-18 were processed for the GMP optimization of CSSC culture and QC assay development, while CSSCs from the remaining 6 were raised under GMP-optimized conditions and used for QC validation. The cell viability, growth, substrate adhesion, stem cell phenotypes, and differentiation into stromal keratocytes were assayed by monitoring the electric impedance changes using xCELLigence real-time cell analyzer, quantitative PCR, and immunofluorescence. CSSC's conditioned media were tested for the anti-inflammatory activity using an osteoclastogenesis assay with mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells. In vivo scar inhibitory outcomes were verified using a mouse model of anterior stromal injury caused by mechanical ablation using an Algerbrush burring.
RESULTS: By comparatively assessing various GMP-compliant reagents with the corresponding non-GMP research-grade chemicals used in the laboratory-based protocols, we finalized GMP protocols covering donor limbal stromal tissue processing, enzymatic digestion, primary CSSC culture, and cryopreservation. In establishing the in vitro QC metric, two parameters-stemness stability of ABCG2 and nestin and anti-inflammatory ability (rate of inflammation)-were factored into a novel formula to calculate a Scarring Index (SI) for each CSSC batch. Correlating with the in vivo scar inhibitory outcomes, the CSSC batches with SI < 10 had a predicted 50% scar reduction potency, whereas cells with SI > 10 were ineffective to inhibit scarring.
CONCLUSIONS: We established a full GMP-compliant protocol for donor CSSC cultivation, which is essential toward clinical-grade cell manufacturing. A novel in vitro QC-in vivo potency correlation was developed to predict the anti-scarring efficacy of donor CSSCs in treating corneal opacities. This method is applicable to other cell-based therapies and pharmacological treatments.